* Add new gifs for crud builder * Add links * Update object-inheritance * Update variables context file with gif and link. Add object inheritance images. * Update variable environments article.
93 lines
3.8 KiB
Markdown
93 lines
3.8 KiB
Markdown
# Using Context Variables
|
|
|
|
Context variables allow you to dynamically store and share data between steps in a scenario. Contrary to environment variables, context variables are _not_ saved once a test has completed. Therefore, context variables are only suitable for temporary data.
|
|
|
|
Context variables are scoped to the scenario, _not_ the collection. This means that two scenarios can both read/write the same context variable `myVar`, and not conflict with each other. Environment variables, on the other hand, are shared amongst all scenarios, and are scoped to the collection.
|
|
|
|
At the start of a test run, the context object is empty. Good examples of data to store in a context would be things like ID's, usernames, and randomly generated tokens.
|
|
|
|
## Use Case
|
|
|
|
Context variables make it possible to chain related steps together. For example, say we have the following set of actions to perform:
|
|
|
|
1. Create User, `POST /users`. Returns a new user object, with an `id` property.
|
|
2. Get User, `GET /users/{$.ctx.userId}`.
|
|
3. Delete User, `DELETE /users/{$.ctx.userId}`.
|
|
|
|
Somehow we need to use the `id` property for the user created in step #1 to build the request in steps #2 and #3. This is a great case for context variables, since the data is temporary (the new user's id changes every test run, and is only needed in this single scenario).
|
|
|
|
To accomplish this, we would capture/set the `$.ctx.userId` property to `output.id` in step #1, and then use that variable to create the request urls in #2 and #3 (shown above).
|
|
|
|
## Setting Context Variables
|
|
|
|
### With Captures
|
|
|
|
The capture UI in the step editor makes it easy to set `$.ctx` values. You can use values from the step output or input, including headers, response bodies, etc.
|
|
|
|
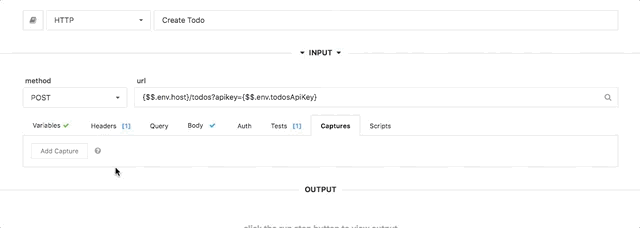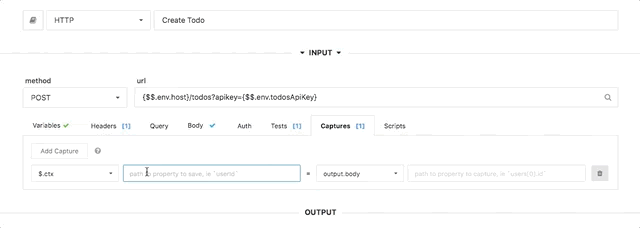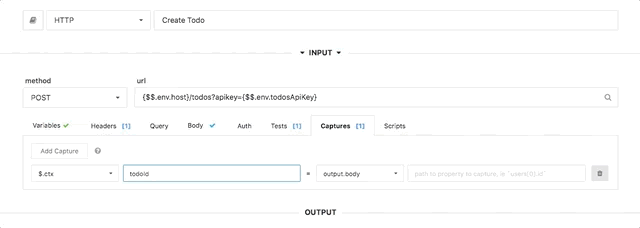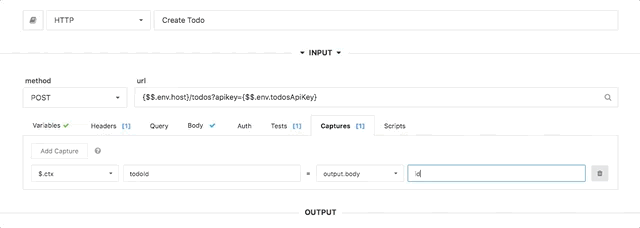
|
|
|
|
> Multiple captures can be applied to the same step, to set multiple `$.ctx` values.
|
|
|
|
### With Scripting
|
|
|
|
Scripting allows you to use more complicated logic in a scenario step. Scripts
|
|
are executed either before or after a step request finishes. Scripts are plain
|
|
Javascript and give you direct access to the scenario context through the global
|
|
`$.ctx` object.
|
|
|
|
For example, if we wanted to set the `userId` property as described in the use case above, we would add an after script to the first step with the code:
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
// store the step output body's 'id' property in the context, for use in subsequent steps
|
|
$.ctx.set('userId', output.body.get('id'));
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Where the `$.ctx.set(x, y)` function adds the data referenced in the second
|
|
argument (`y`) to the context under the string value of the first argument
|
|
(`x`).
|
|
|
|
Here is another example that just sets `myVariable` to the hardcoded value `123`:
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
$.ctx.set('myVariable', 123);
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
## Using Context Variables
|
|
|
|
To use a context variable in a scenario, use the following syntax:
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
{$.ctx.myVariable}
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Where:
|
|
|
|
* `{...}` - Braces signify that this is a variable.
|
|
* `$` - The "single dollar sign" syntax is a reference to the current scenario's
|
|
runtime scope. Again, context variables are scoped to the individual scenario, not the global collection!
|
|
* `ctx` - This is the actual context object onto which values are stored and retrieved.
|
|
* `myVariable` - This is the name of the variable being referenced within the context.
|
|
|
|
When the scenario or step is run, all context variables will
|
|
automatically be populated based on the contents of the `$.ctx` at
|
|
runtime.
|
|
|
|
### In Scripts
|
|
|
|
Similar to the example above, when referencing a context variable in a step
|
|
script, use the following syntax:
|
|
|
|
```javascript
|
|
$.ctx.get('myVariable');
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
Where the braces (`{}`) are absent, and we are using the `get()` method for
|
|
retrieving the context variable under the `myVariable` key.
|
|
|
|
---
|
|
|
|
**Related Articles**
|
|
|
|
* [Using Variables Overview](/testing/using-variables/overview)
|
|
* [$$.env (Environment)](/testing/using-variables/environment)
|